A recreational vehicle’s heating system failure can manifest in various ways, from a complete lack of warm air to intermittent operation or unusual noises. This can stem from several potential issues, including problems with the thermostat, igniter, gas supply, or electrical components. A non-functional heating system in an RV can impact comfort and safety, particularly during colder weather conditions.
Reliable heating is essential for comfortable and safe RV travel, especially in colder climates or during the winter months. A functioning furnace allows occupants to maintain a comfortable living environment and prevents potential issues such as frozen water lines. Historically, RV heating systems have evolved from simple propane heaters to more complex and efficient forced-air furnaces, reflecting a growing demand for comfort and reliability in mobile living.
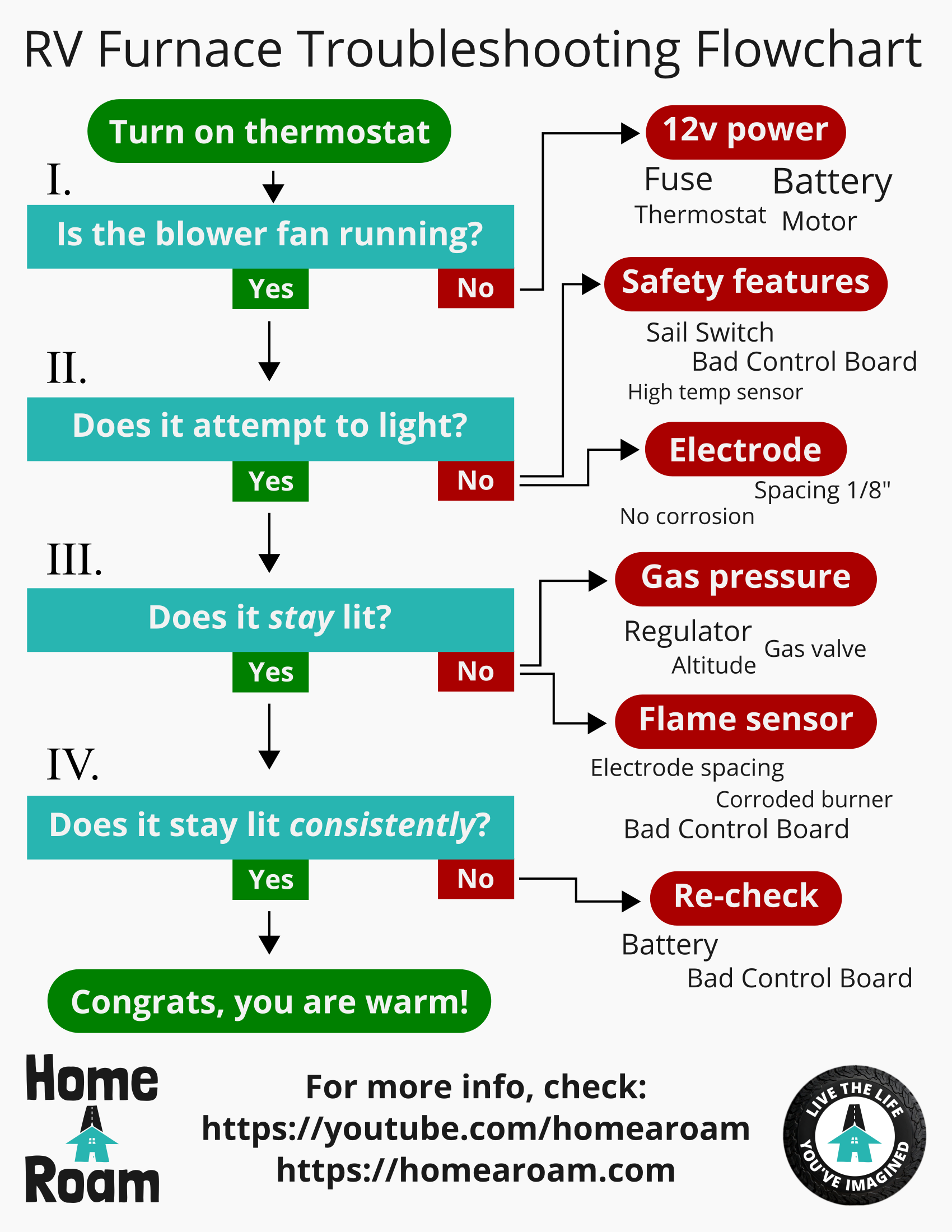
Understanding the potential causes of heating system malfunctions, along with troubleshooting and maintenance procedures, is crucial for RV owners. The following sections will explore common reasons for these failures, diagnostic techniques, and potential solutions.
1. Power Supply
A consistent and adequate power supply is essential for RV furnace operation. Furnaces rely on electricity to power various components, including the control board, blower motor, and igniter. Without sufficient power, the furnace may fail to ignite, run intermittently, or not function at all. A common cause of power-related furnace issues is a tripped circuit breaker or blown fuse. This can occur due to a power surge, a malfunctioning furnace component, or an overloaded circuit. For instance, if the blower motor draws excessive current due to worn bearings, it could trip the breaker, interrupting power to the furnace.
Troubleshooting power supply problems involves checking the RV’s electrical panel for tripped breakers or blown fuses. If a breaker trips repeatedly, it may indicate a deeper issue with the furnace itself, requiring professional diagnosis. Using a multimeter to verify voltage at the furnace’s electrical connections can help pinpoint wiring problems. Furthermore, low voltage conditions in the RV’s electrical system can also impact furnace performance. For example, if the RV’s battery is low, the furnace may not receive sufficient power to operate reliably, even if the shore power connection is active.
Ensuring a stable power supply is crucial for reliable furnace operation. Regularly checking the electrical system, including breakers, fuses, and wiring, can prevent power-related furnace failures. Understanding the relationship between the furnace and the RV’s electrical system allows for effective troubleshooting and helps maintain a comfortable and safe environment within the vehicle, particularly during colder weather conditions. Addressing power supply issues proactively can prevent inconvenient and potentially hazardous situations while traveling.
2. Propane Supply
Propane serves as the primary fuel source for many RV furnaces. A sufficient and consistent propane supply is therefore critical for proper furnace operation. Any interruption or inadequacy in this supply can directly lead to heating failures, ranging from inefficient heating to complete furnace shutdown. Understanding the various components and potential issues within the propane supply system is essential for effective troubleshooting.
-
Propane Level
The most common cause of propane-related furnace issues is simply an insufficient propane level in the tank. A low propane level can prevent the furnace from igniting or cause it to shut down prematurely. Regularly checking the propane tank gauge is crucial, especially before and during trips. For example, a near-empty tank on a cold night can leave occupants without heat. Monitoring propane levels proactively can prevent such scenarios.
-
Propane Regulator
The propane regulator controls the flow of propane from the tank to the furnace. A malfunctioning regulator can restrict propane flow, leading to inadequate furnace performance or failure to ignite. Symptoms of a faulty regulator might include flickering or weak flames on other propane appliances, such as the stovetop. Regulator failure can occur due to age, wear, or damage. Replacing a faulty regulator is often necessary to restore proper propane flow.
-
Gas Leaks
Propane leaks pose a serious safety hazard and can contribute to furnace malfunction. Leaks can occur in the propane tank, connecting lines, or within the furnace itself. A distinct odor, similar to rotten eggs, often indicates a propane leak. In the event of a suspected leak, immediately turn off the propane supply at the tank and evacuate the RV. Professional inspection and repair are essential to address any leaks and ensure safe operation.
-
Obstructions in Propane Lines
Debris or other obstructions within the propane lines can restrict propane flow to the furnace. This can result in reduced furnace output or complete failure. While less common than other propane-related issues, obstructions can occur due to rust, insect nests, or foreign material entering the lines. Troubleshooting this involves inspecting and clearing any blockages in the propane lines.
Addressing propane supply problems effectively requires a systematic approach. Checking the propane level, inspecting the regulator, and ensuring the absence of leaks are crucial steps in diagnosing and resolving furnace issues related to propane. Maintaining a consistent and safe propane supply is vital not only for reliable furnace operation but also for overall RV safety and functionality. Neglecting these aspects can jeopardize comfort and potentially create hazardous situations, especially during colder weather conditions.
3. Ignition System
The ignition system plays a vital role in the operation of an RV furnace, responsible for igniting the propane to generate heat. A malfunctioning ignition system is a frequent cause of furnace failure. Understanding its components and how they interact is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
-
Electronic Ignition Control Modules
Modern RV furnaces typically employ electronic ignition control modules. These modules manage the ignition sequence, controlling the spark generation and gas valve operation. A faulty control module can disrupt this sequence, preventing the furnace from igniting. For example, a malfunctioning module might fail to send the signal to open the gas valve, or it might generate a weak or inconsistent spark. Replacing the control module is often the solution when these issues occur.
-
Igniters: Spark vs. Direct Spark Ignition (DSI)
RV furnaces utilize either a spark igniter or a direct spark igniter (DSI). Spark igniters generate a high-voltage spark between two electrodes, similar to a spark plug, to ignite the propane. DSIs, on the other hand, utilize a high-voltage electrode near the burner to directly ignite the gas. A common problem with spark igniters is electrode wear or cracking, which can weaken the spark or prevent it from occurring altogether. DSIs can also fail due to electrode wear, contamination, or control module issues. Replacing a faulty igniter often restores functionality.
-
Flame Sensor
The flame sensor is a critical safety component within the ignition system. Its purpose is to detect the presence of a flame after ignition. If the flame sensor does not detect a flame, it signals the control module to shut off the gas supply, preventing a potentially dangerous buildup of unburned propane. A malfunctioning flame sensor can cause the furnace to cycle on and off repeatedly or fail to ignite altogether. Dirt, soot, or corrosion can accumulate on the flame sensor, hindering its ability to detect the flame. Cleaning or replacing the flame sensor often resolves these issues.
-
Limit Switches and Sail Switches
Limit switches and sail switches act as safety mechanisms within the furnace system. Limit switches protect the furnace from overheating by shutting it down if the temperature exceeds a safe limit. Sail switches ensure proper airflow through the furnace. If airflow is insufficient, the sail switch will prevent the furnace from igniting, protecting it from damage. A malfunctioning limit switch or sail switch can prevent the furnace from operating even if the ignition system is functioning correctly. Testing and replacing these switches are necessary when they fail.
A properly functioning ignition system is essential for reliable RV furnace operation. Failure within any component of this system can lead to heating issues, ranging from inefficient operation to complete failure. Understanding the roles of the electronic control module, igniter, flame sensor, and safety switches, along with common failure points, allows for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. Addressing ignition system problems proactively ensures a safe and comfortable environment within the RV, especially during colder weather conditions. Ignoring these issues can lead to inconvenient breakdowns and potentially create hazardous situations.
4. Thermostat
The thermostat acts as the control center for the RV furnace, regulating the temperature and signaling the furnace when to turn on and off. A malfunctioning thermostat is a common culprit when an RV furnace fails to operate as expected. Understanding its function and potential issues is essential for effective troubleshooting.
-
Temperature Setting Accuracy
The thermostat’s primary function is to maintain the desired temperature within the RV. If the thermostat is not accurately reading the ambient temperature, it may fail to signal the furnace to turn on or off appropriately. For example, a thermostat calibrated incorrectly might read a temperature higher than the actual temperature, preventing the furnace from activating even when the RV is cold. Verifying the thermostat’s accuracy against a known reliable thermometer is essential in diagnosing such issues.
-
Anticipation Circuit
Many RV thermostats include an anticipation circuit designed to prevent temperature overshoot. This circuit slightly overheats the thermostat’s internal sensor, causing the furnace to shut off slightly before reaching the set temperature. A malfunctioning anticipation circuit can lead to temperature fluctuations or prevent the furnace from reaching the desired temperature. Adjusting the anticipation setting or replacing the thermostat may be necessary if this circuit is faulty.
-
Wiring and Connections
The thermostat communicates with the furnace through low-voltage wiring. Loose or damaged wiring can disrupt this communication, preventing the thermostat from effectively signaling the furnace. For instance, a corroded wire connection could prevent the thermostat’s “on” signal from reaching the furnace. Inspecting and repairing any wiring issues is essential to ensure proper communication between the thermostat and the furnace.
-
Thermostat Compatibility
Different types of RV furnaces require compatible thermostats. Using an incompatible thermostat can lead to operational issues or prevent the furnace from functioning altogether. For example, attempting to use a millivolt thermostat with a furnace designed for a digital thermostat can lead to control issues. Ensuring thermostat compatibility with the specific furnace model is crucial for proper operation. Consulting the furnace and thermostat documentation can confirm compatibility.
The thermostat is a critical component in the operation of an RV furnace. Addressing any thermostat-related issues is essential for maintaining a comfortable and functional heating system. Understanding the role of the thermostat, its potential failure points, and its interaction with the furnace allows for effective troubleshooting and repair. By ensuring the thermostat is functioning correctly, RV owners can maintain a consistent and comfortable temperature within their vehicles, especially during colder weather conditions, and avoid potential furnace-related problems.
5. Airflow
Adequate airflow is essential for the safe and efficient operation of an RV furnace. Restricted or obstructed airflow can lead to a variety of issues, including overheating, inefficient heating, and even complete furnace shutdown. Understanding the components and factors that influence airflow is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining a functional heating system.
-
Return Air Intake
The return air intake draws cool air from inside the RV back into the furnace. Obstructions at the return air intake, such as furniture, carpeting, or debris, can significantly restrict airflow. This reduced airflow can starve the furnace of the air needed for combustion and heat exchange, leading to inefficient heating or furnace shutdown. For example, a rug placed over the return air vent can drastically reduce air intake, impacting furnace performance.
-
Ductwork and Venting
The ductwork and venting system distribute heated air throughout the RV and exhaust combustion byproducts. Crushed, blocked, or disconnected ducts can impede airflow, reducing heating efficiency and potentially causing dangerous backflow of exhaust gases. For instance, a collapsed duct in the underbelly of the RV can restrict airflow to a specific area and cause heat to back up, potentially overheating the furnace. Regular inspection and cleaning of the ductwork are essential for maintaining proper airflow.
-
Blower Motor
The blower motor propels heated air through the ductwork and into the RV’s living space. A malfunctioning blower motor, such as one with worn bearings or a damaged fan blade, can significantly reduce airflow. This can result in weak or inconsistent heating, or in some cases, no heat at all. For example, a seized blower motor will completely stop airflow, rendering the furnace ineffective. Regular maintenance, including lubrication and inspection of the blower motor, is important for reliable operation.
-
Combustion Air Intake
The combustion air intake supplies fresh air to the furnace for proper combustion. This intake is typically located on the exterior of the RV. Blockages at the combustion air intake, such as snow, ice, or debris, can restrict the oxygen supply to the furnace, leading to incomplete combustion and the production of dangerous carbon monoxide. Maintaining a clear and unobstructed combustion air intake is critical for safe furnace operation.
Proper airflow is paramount for a functioning RV furnace. Restrictions or obstructions in any part of the airflow system can negatively impact furnace efficiency, safety, and overall performance. Addressing airflow issues promptly, from cleaning vents and ducts to ensuring a functioning blower motor and unobstructed intakes, is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and safe environment within the RV, especially during colder weather conditions. Neglecting these aspects can lead to inefficient heating, potential furnace damage, and even dangerous situations due to carbon monoxide buildup.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding RV furnace malfunctions.
Question 1: Why does the RV furnace keep turning on and off?
Short cycling can be caused by several factors, including a dirty flame sensor, restricted airflow, a faulty thermostat, or an overheating limit switch. Troubleshooting each of these potential issues is necessary to identify the root cause.
Question 2: What should be done if the RV furnace smells like gas?
A gas odor indicates a potential leak, which is a serious safety hazard. Turn off the propane supply at the tank immediately, evacuate the RV, and contact a qualified RV technician to inspect and repair the leak.
Question 3: How often should an RV furnace be serviced?
Annual professional inspection and servicing are recommended. This typically includes cleaning, inspecting components like the igniter and flame sensor, and verifying proper operation. Regular maintenance can prevent many common furnace problems.
Question 4: Can the RV furnace be used while driving?
While technically possible, using the furnace while driving consumes significant propane and may not be efficient due to air movement around the RV. It’s generally more efficient to use the vehicle’s engine heat for warmth while traveling.
Question 5: What are signs of a clogged furnace burner?
A clogged burner can manifest as a yellow or flickering flame, reduced heat output, or sooty buildup around the burner. Professional cleaning is recommended to remove any obstructions and restore proper burner function.
Question 6: Why is the RV furnace blowing cold air?
Several factors can cause cold air discharge, including a lack of propane, a faulty igniter, a malfunctioning blower motor, or a problem with the thermostat. Systematic troubleshooting is needed to pinpoint the exact cause.
Addressing these common concerns proactively can contribute to the reliable operation of the RV furnace. Consulting a qualified RV technician is recommended when troubleshooting complex issues or when safety concerns arise.
The following section provides additional resources for maintaining and troubleshooting RV furnace issues.
Troubleshooting Tips for RV Furnace Malfunctions
These troubleshooting tips offer practical guidance for addressing common RV furnace issues. Systematic investigation is crucial for identifying the root cause of heating system failures. Safety precautions should always be observed when working with propane and electrical systems.
Tip 1: Verify Power Supply: Begin by checking the RV’s circuit breakers and fuses. A tripped breaker or blown fuse often interrupts power to the furnace. Resetting the breaker or replacing the fuse may restore functionality. If the issue persists, further investigation of the electrical system may be necessary.
Tip 2: Inspect Propane Levels: Ensure an adequate propane supply exists. Low propane levels can prevent furnace ignition. Check the propane tank gauge and refill the tank if necessary. Consider potential issues with the propane regulator if adequate propane exists but the furnace still fails to ignite.
Tip 3: Examine the Exhaust Vent: Obstructions in the furnace exhaust vent can prevent proper operation. Inspect the vent for blockages such as debris, snow, or ice. Clear any obstructions to ensure unrestricted exhaust flow.
Tip 4: Check the Thermostat: Verify the thermostat is set correctly to a heating mode and the desired temperature. A faulty thermostat can prevent the furnace from activating. Test the thermostat’s accuracy against a known reliable thermometer. Consider replacing the thermostat if necessary.
Tip 5: Inspect the Furnace Air Filter: A dirty or clogged air filter restricts airflow and hinders furnace performance. Regularly replace or clean the furnace air filter according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. This ensures sufficient airflow for combustion and heat exchange.
Tip 6: Listen for Unusual Noises: Unusual noises emanating from the furnace, such as grinding or squealing, can indicate mechanical problems. These noises may suggest issues with the blower motor or other internal components. Investigate the source of any unusual sounds and address the underlying mechanical issues.
Tip 7: Check the Ignition System: If the furnace receives power and adequate propane but fails to ignite, the ignition system may be faulty. This could involve the igniter, flame sensor, or control board. Inspect these components for damage or malfunction. Cleaning the flame sensor or replacing a faulty igniter may resolve ignition problems.
Tip 8: Consult a Qualified Technician: If troubleshooting efforts do not resolve the furnace issue, consult a qualified RV technician. Complex problems may require professional diagnosis and repair. Attempting repairs beyond one’s expertise can exacerbate the issue or create safety hazards.
Systematic troubleshooting, coupled with appropriate safety measures, can effectively address many common RV furnace problems. Professional assistance should be sought when dealing with complex issues or gas leaks. Proper maintenance and preventative measures contribute significantly to the longevity and reliable operation of the RV’s heating system.
This compilation of troubleshooting tips aims to empower RV owners with the knowledge to address common furnace malfunctions. The following conclusion provides a summary of key takeaways and reinforces the importance of proper furnace maintenance.
Conclusion
A malfunctioning RV furnace presents significant challenges to comfortable and safe travel, especially during colder seasons. This exploration has examined various facets of this issue, from understanding the underlying causes related to power supply, propane delivery, ignition systems, thermostats, and airflow, to providing practical troubleshooting tips and addressing frequently asked questions. Systematic diagnosis and appropriate maintenance are essential for reliable furnace operation. Recognizing the interconnectedness of these components allows for effective problem-solving and preventative measures.
Reliable heating is paramount for a safe and enjoyable RV experience. Proactive maintenance, coupled with a thorough understanding of potential issues, empowers RV owners to address challenges effectively and ensure consistent warmth and comfort during travels. Neglecting furnace maintenance can lead to inconvenient breakdowns and potentially hazardous situations. Prioritizing regular inspections and timely repairs ensures a dependable heating system and contributes to a positive and worry-free RV experience. Professional assistance should always be sought when encountering complex issues or safety concerns involving gas leaks or electrical malfunctions.



